¶ API documentation
- Overview
- Update data with PUT request
- Splynx PHP API template with examples
- Splynx API
- How to use the search with the operator IN
- How to attach two files into a ticket
¶ Overview
This section redirects you to the Splynx API documentation website:
Splynx API documentation website
¶ Update data with PUT request
Sometimes, you need to update data, and our API requires a PUT request. For example, refer to Update a Customer info
In this case, you should use the following settings:
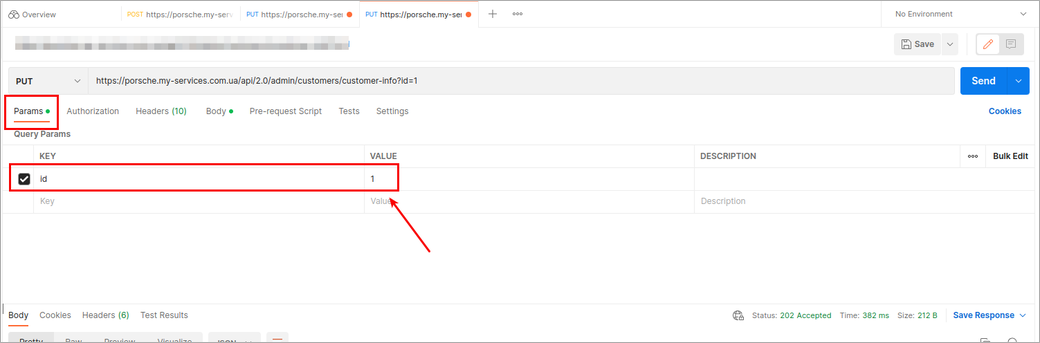
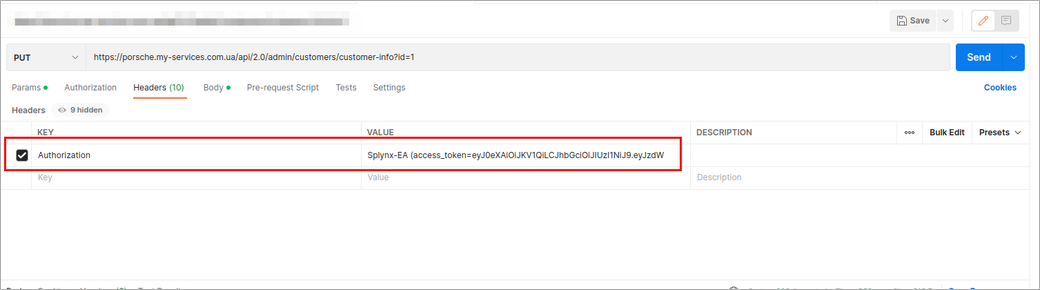
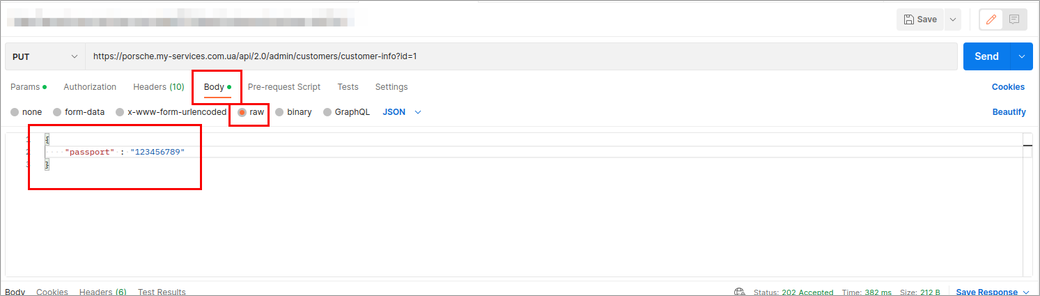
¶ Splynx PHP API template with examples
For the developers, it's recommended to check this template (splynx-php-api/src → SplynxApi.php and the files in splynx-php-api/examples), it provides useful methods on how to make queries to the Splynx API.
If you have already installed the Splynx system, you can find the same template on your server, just navigate to /var/www/splynx/addons/splynx-addon-base-2/vendor/splynx/splynx-php-api location.
For more information about the Splynx API, see our wiki page: https://api-doc.splynx.com/
PHP module with examples - https://bitbucket.org/splynx/splynx-php-api/src/master/
¶ Splynx API
Splynx system has its own Application Programming Interface (API) which allows software applications to communicate with each other via API calls. In order to simplify the workflow with Splynx API in testing and development you can use Postman. Postman - is an open source tool and can be easily downloaded here according to your desired platform. After install the app and sign up for account you can start work on Postman startup screen.
To get started with the Postman app, please check this documentation.
Splynx supports the following type of authentication:
¶ Access by token
- Authentication as admin
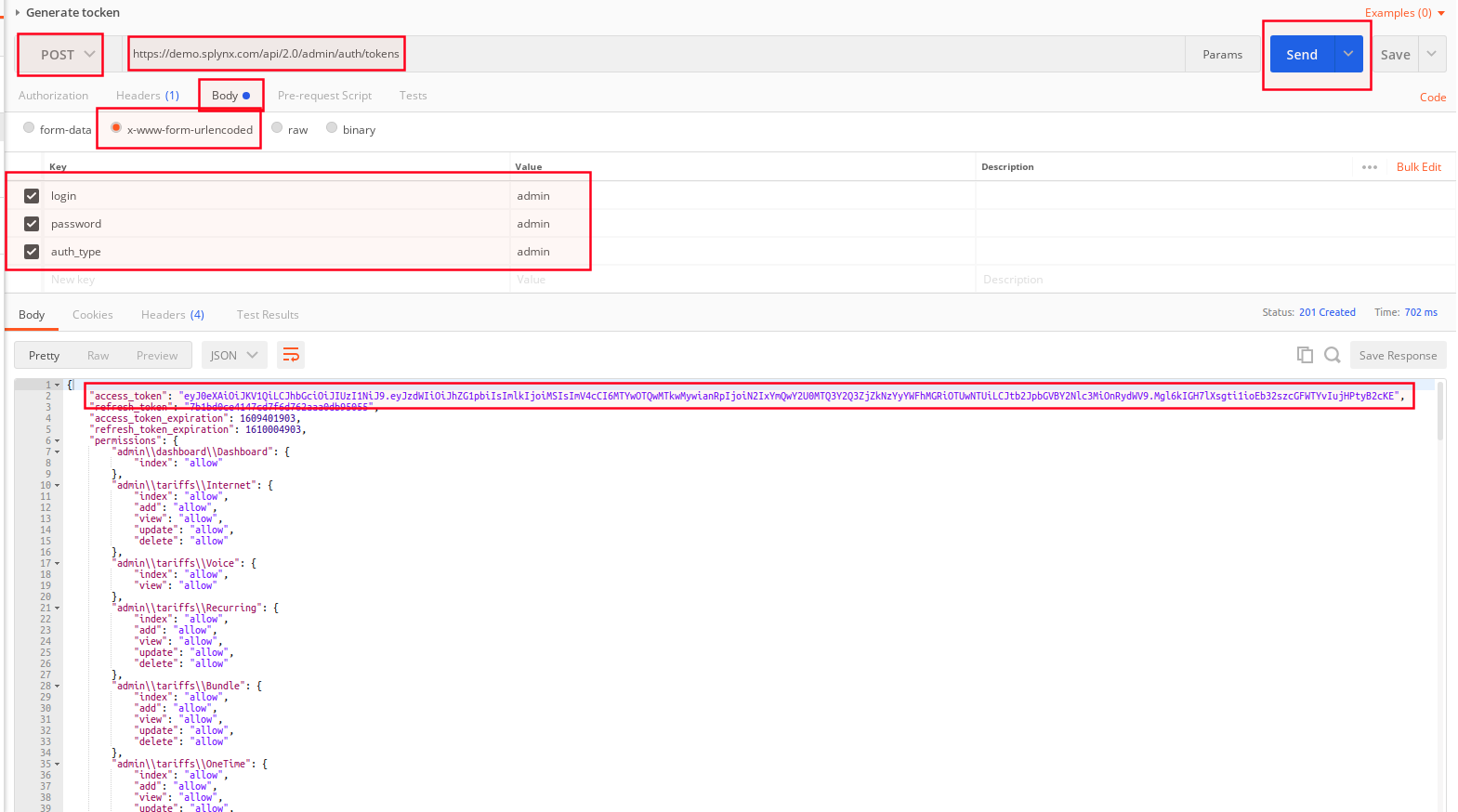
Generate the token for authorization and send GET request. Required fields: login, password. Please note that it's necessary to create an admin user account in Splynx and assign the role e.g. super administrator, it depends on what the access rights you need.
The request method (verb) determines the nature of action you intend to perform.
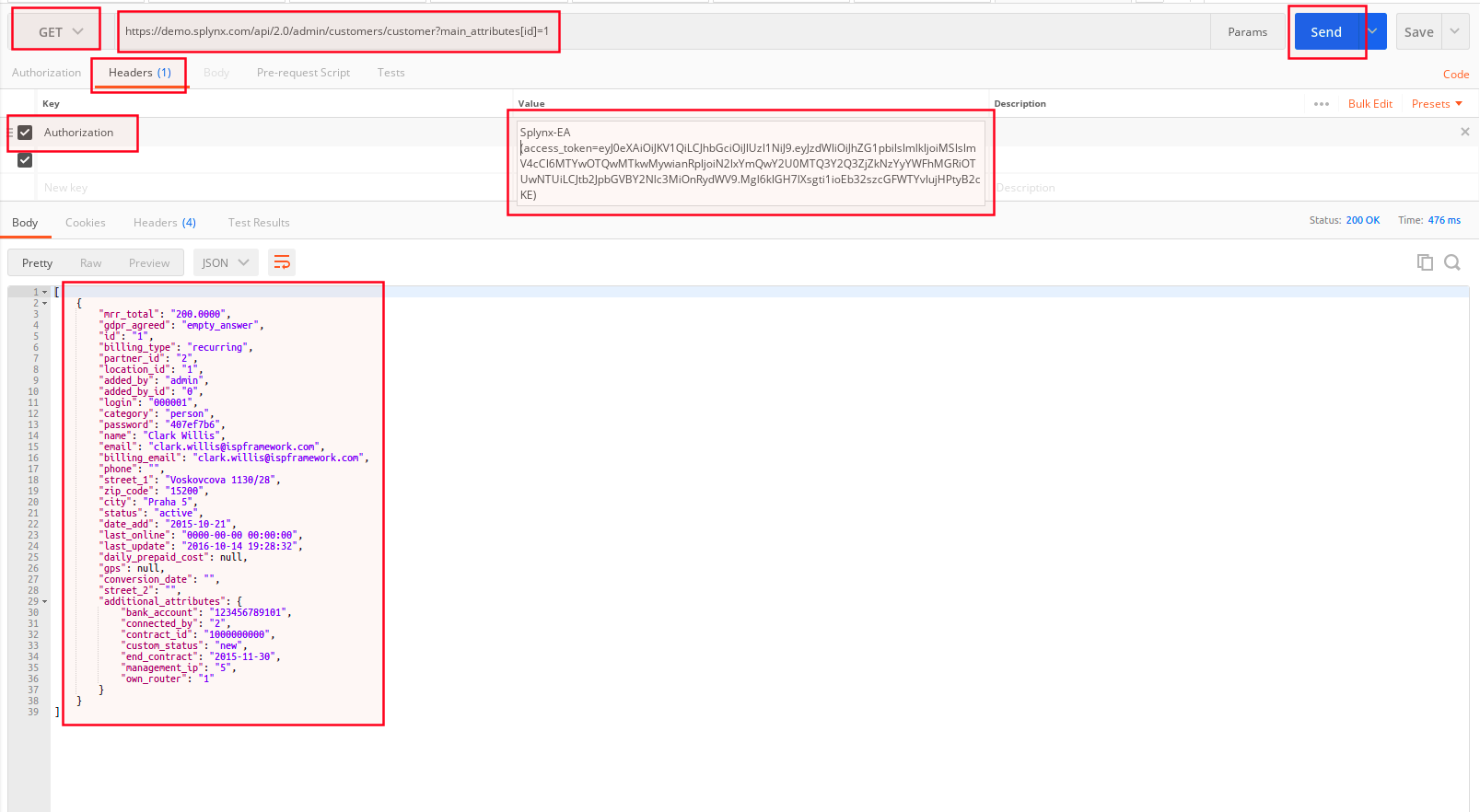
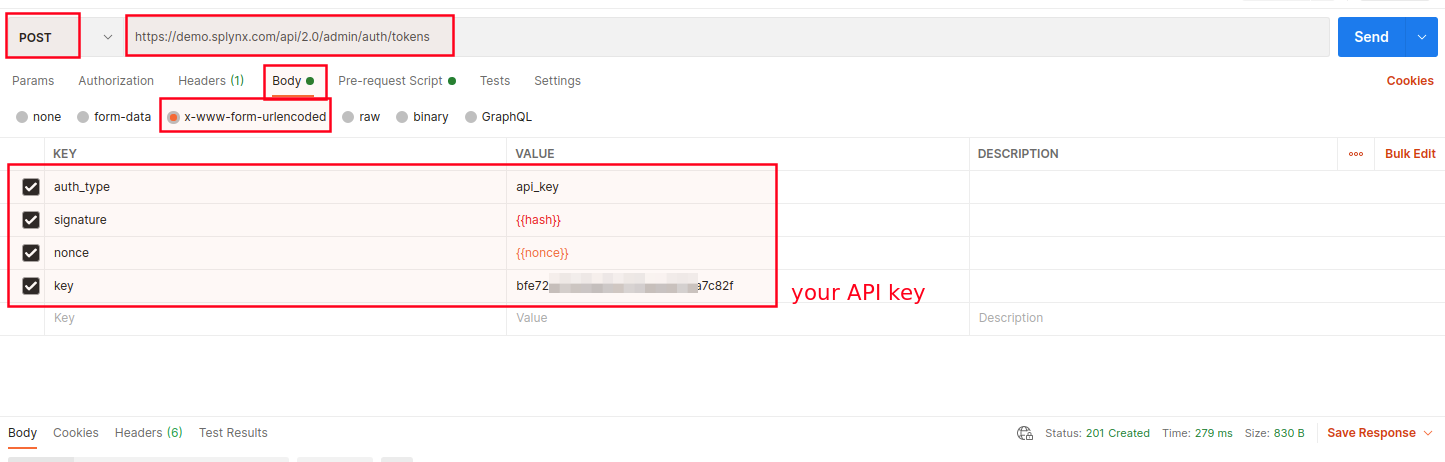
- Authentication by API key
Create a new request in Postman, specify its details such as method GET, request URL and keys.
Required fields: auth_type, signature, nonce, key.
Where key - is your API key, nonce - a current timestamp in seconds.
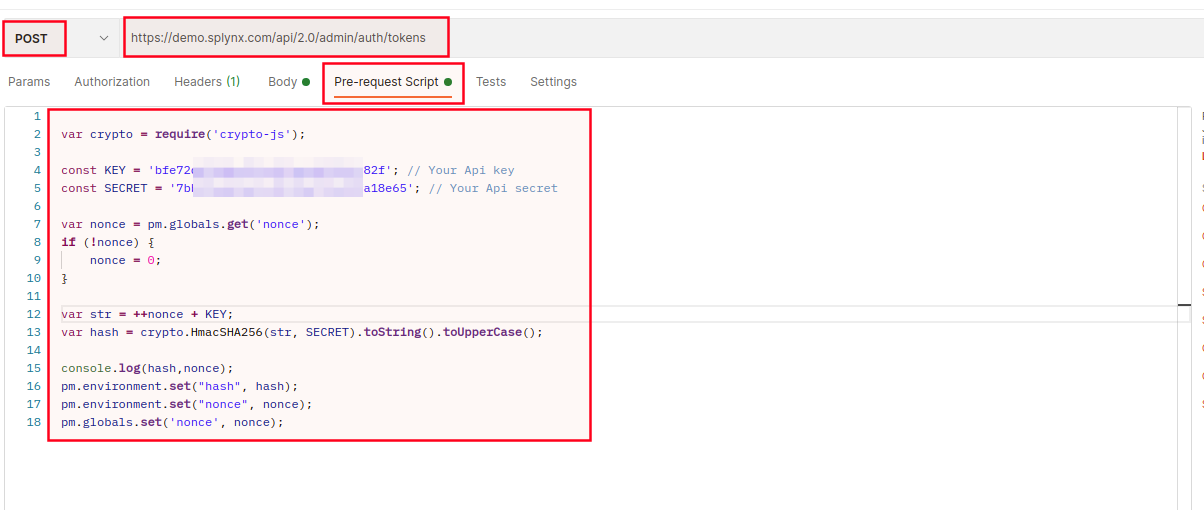
Then, create pre-request script in Postman, for example:
var crypto = require('crypto-js');
const KEY = 'bfe72xxxxxxxxxxa123bdc8e78a7c82f'; // Your Api key
const SECRET = '7bxxxxxxxxxxc4332567c8afdfa18e65'; // Your Api secret
var nonce = pm.globals.get('nonce');
if (!nonce) {
nonce = 0;
}
var str = ++nonce + KEY;
var hash = crypto.HmacSHA256(str, SECRET).toString().toUpperCase();
console.log(hash,nonce);
pm.environment.set("hash", hash);
pm.environment.set("nonce", nonce);
pm.globals.set('nonce', nonce);
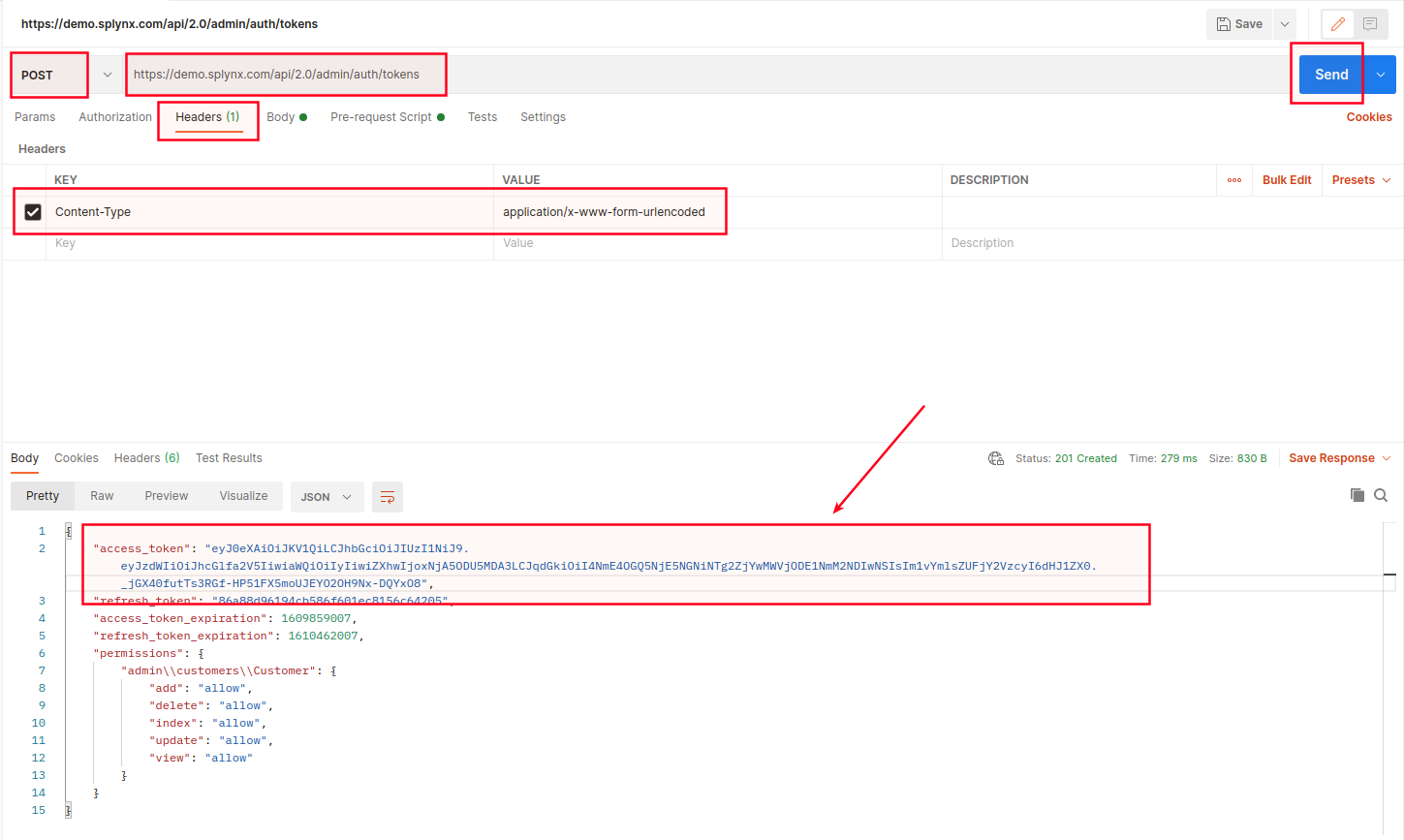
Then, use POST with Content-type to add new data and press Send. Check your access token in body section.
¶ Basic authentication
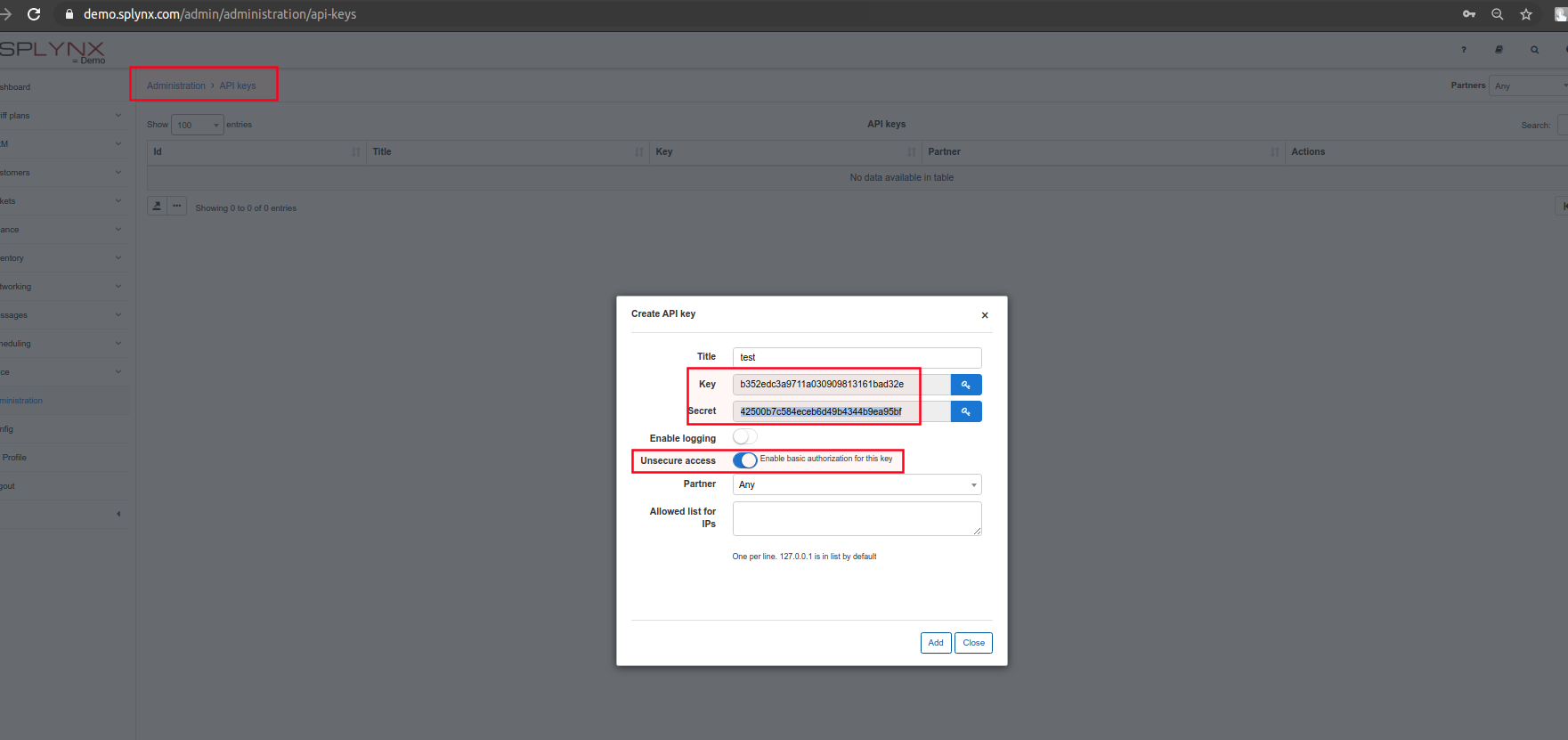
Add API key with Unsecure access in Administaration → API keys;
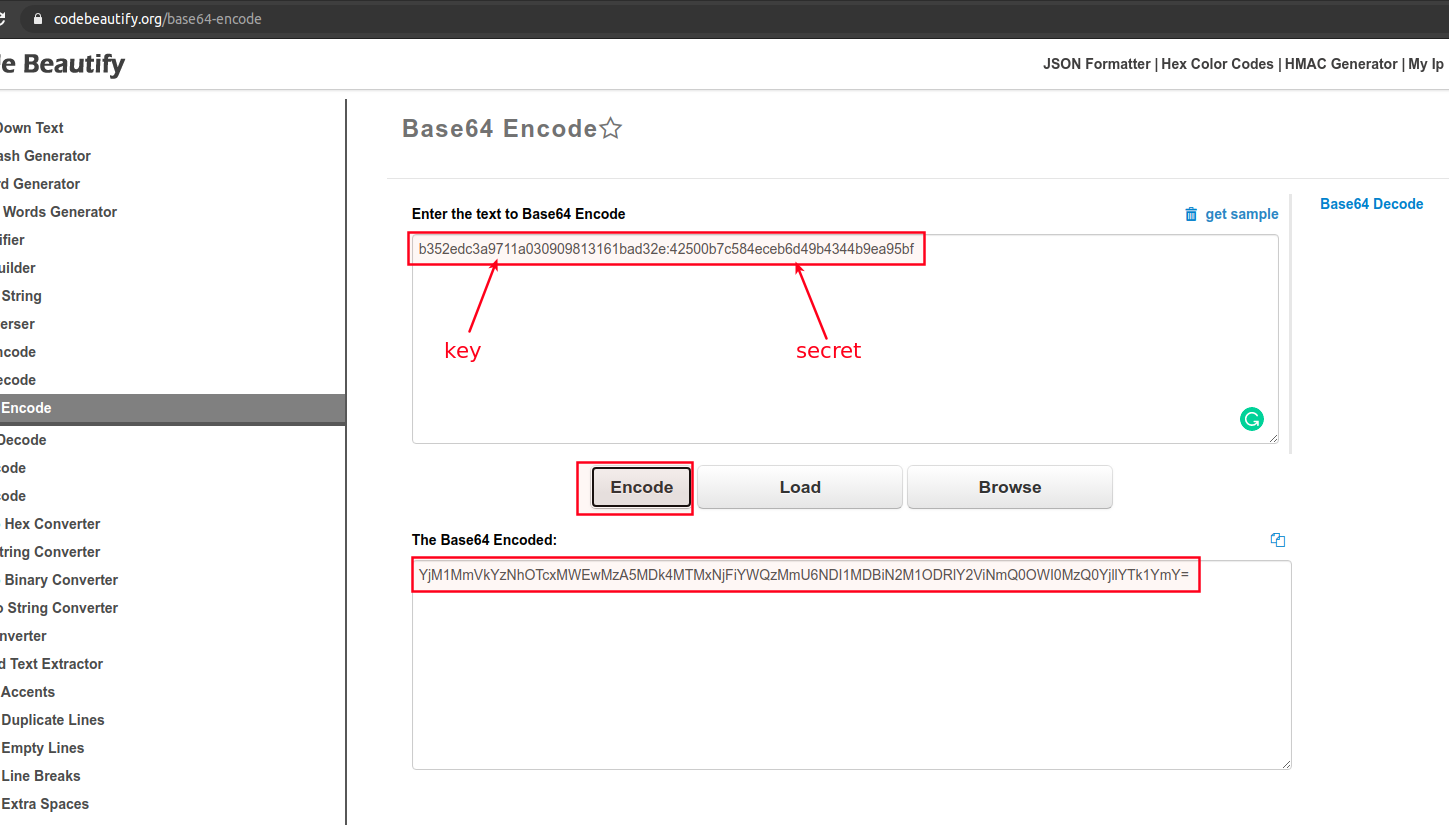
Encode you secret phrase to Base64, for example on this web site;
Copy the encoded text, insert it as a value for Authorization key in Postman and press Send. Check the result in body section.
¶ Access by signature
(Like in API v1)
Create API key and its secret in Administaration → API keys;
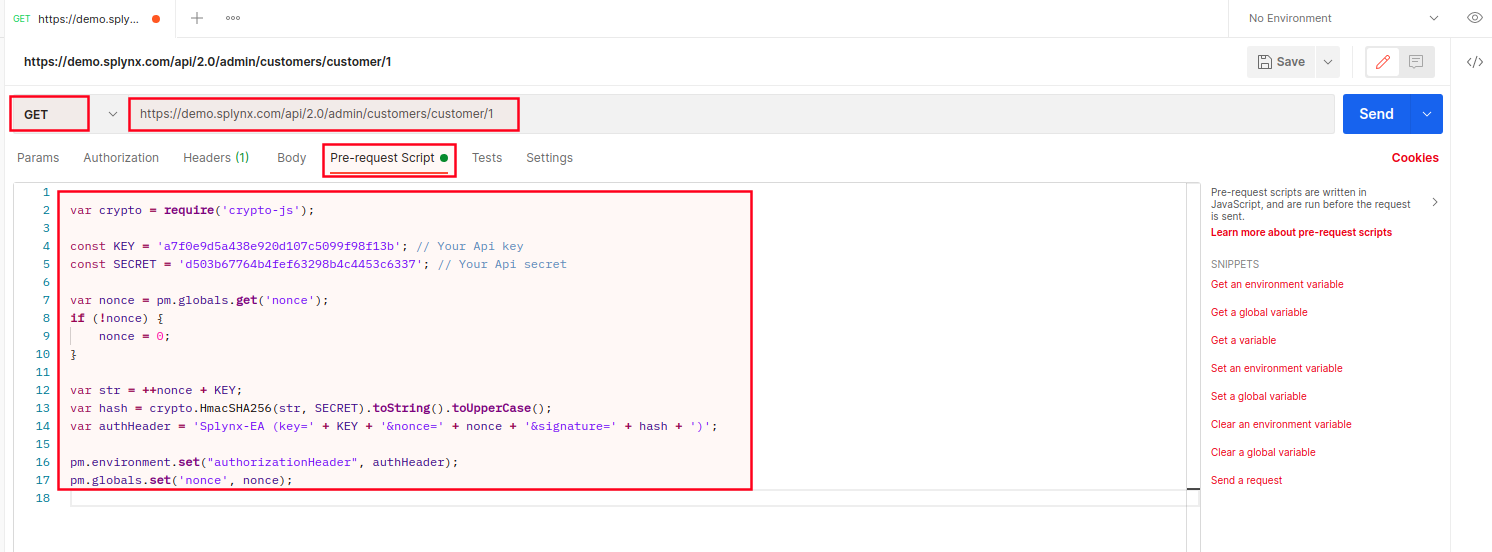
Create pre-request script in Postman, for example:
var crypto = require('crypto-js');
const KEY = 'a7f0e9d5a438e920d107c5099f98f13b'; // Your Api key
const SECRET = 'd503b67764b4fef63298b4c4453c6337'; // Your Api secret
var nonce = pm.globals.get('nonce');
if (!nonce) {
nonce = 0;
}
var str = ++nonce + KEY;
var hash = crypto.HmacSHA256(str, SECRET).toString().toUpperCase();
var authHeader = 'Splynx-EA (key=' + KEY + '&nonce=' + nonce + '&signature=' + hash + ')';
pm.environment.set("authorizationHeader", authHeader);
pm.globals.set('nonce', nonce);
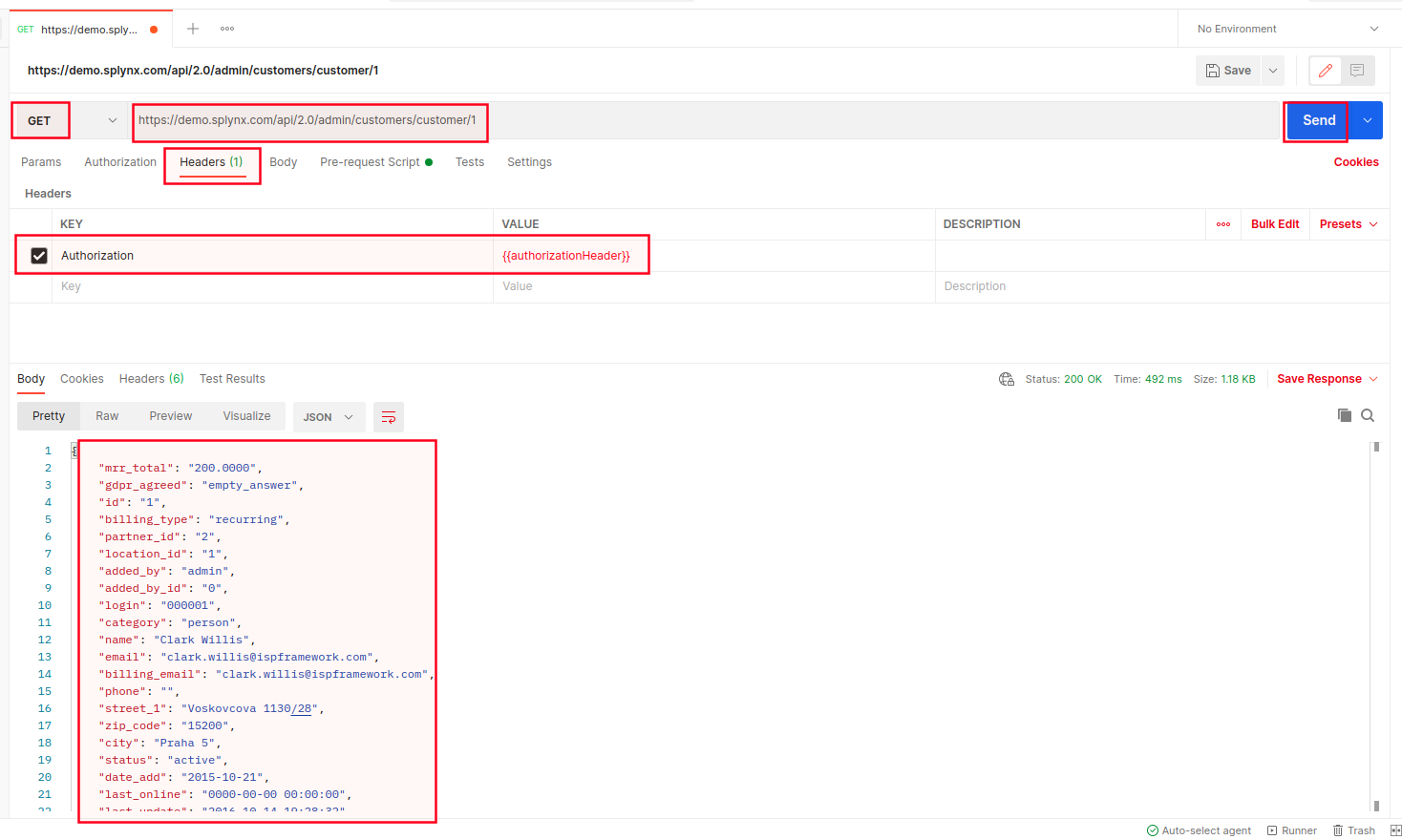
Create autorizaton request with {{authorizationHeader}} value and press Send.
The output results indicate that tests were successful.
¶ API search
Example:
<?php
$params = [
'main_attributes' => [
'login' => ['LIKE', 'durden'],
'partner_id' => ['BETWEEN', 1, 10],
'date_add' => date('Y-m-d'),
'added_by' => 'api',
],
'additional_attributes' => [
'sex' => ['IN', ['male', 'female']],
],
'order' => [
'id' => 'DESC',
],
'limit' => 10,
'offset' => 20,
];
$apiUrl = 'admin/customers/customer' . '?' . http_build_query($params);
All operators list
=!=>=<=><<>ISREGEXPBETWEENLIKEIN'FIND_IN_SET
¶ How to use the search with the operator IN
'main_attributes' => [
'tariff_id' => ['IN', ['2', '1']],
],
REGEXP Operator:
For the 'REGEXP' operator, yes, the second parameter typically is a regular expression string.
Usually, regular expressions don't need the delimiters /.../ in database contexts, but some APIs might expect them.
Example:
https://you_splynx_url/api/2.0/admin/crm/quotes/?main_attributes[id][0]=REGEXP&main_attributes[id][1]=^(?!1|2|3|4|5)
FIND-IN-SET Operator:
The 'FIND-IN-SET' operator typically searches for a value within a comma-separated string.
The second parameter is usually a single value or a comma-separated list of values [...].
BETWEEN Operator:
The 'BETWEEN' operator's functionality can vary based on the data type it's used with.
It can work with numeric ranges, lexicographical comparisons (strings), or dates, depending on how the API is designed.
Example:
<?php
$apiKey = 'YOUR_API_KEY';
$apiUrl = 'https://your_url/api/2.0/admin/customers/customer';
$params = [
'main_attributes' => [
'partner_id' => ['BETWEEN', 1, 3],
'date_add' => [
'BETWEEN',
date('Y-m-01'),
date('Y-m-t')
],
],
];
$queryString = http_build_query($params);
$ch = curl_init();
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, "$apiUrl?$queryString");
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, [
'Authorization: Basic ' . $apiKey,
]);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
echo $response;
?>
Difference between 'FIND-IN-SET' and 'IN':
'FIND-IN-SET' and 'IN' are different operators used for different purposes.
'IN' typically checks if a value exists within a specified set of values or a subquery result.
'FIND-IN-SET' specifically checks if a value exists within a comma-separated string.
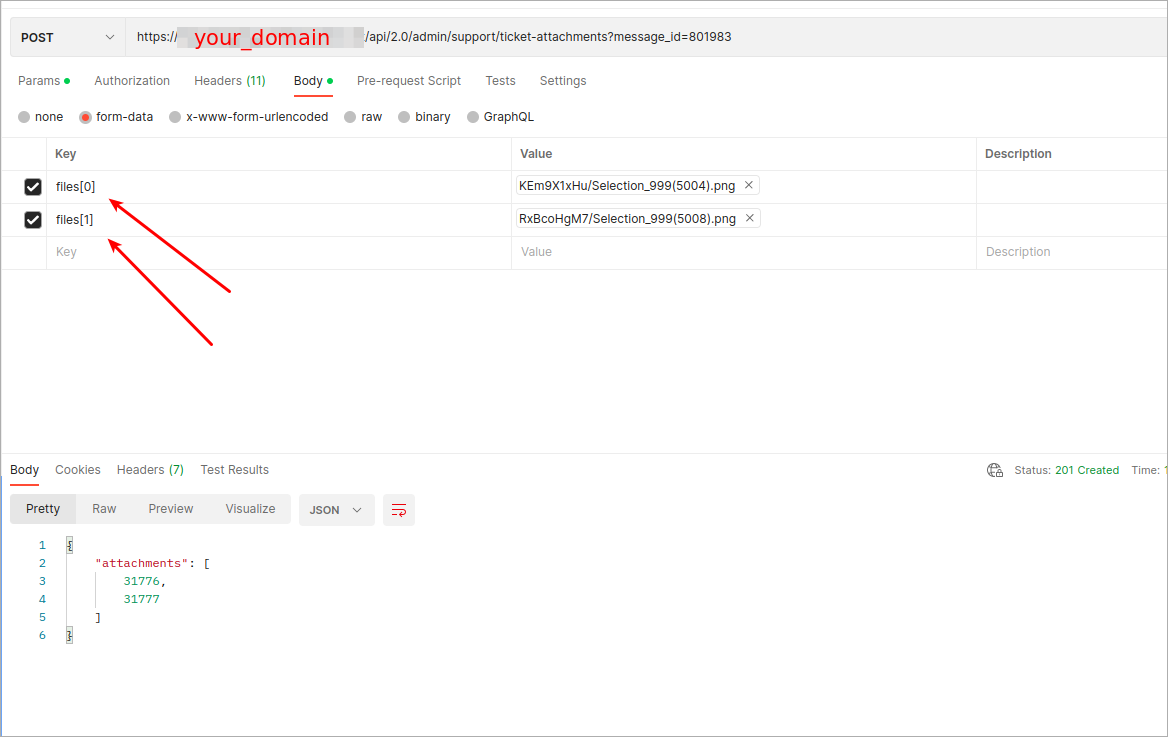
¶ How to attach two files into a ticket